使用C/C++类库控制舵机
如何调用C/C++类库
在控制舵机中,我们展示了如何使用定时器控制波形生成器生成控制舵机的波形。
由于C/C++生态在嵌入式开发场景下,已经比较成熟了,有大量的类库可以使用,那么,本示例中,我们将讲解如何在Rust中调用C/C++类库的类型和方法。
我们需要编写一个build.rs脚本,放在项目根目录下,扩展cargo的编译过程。
硬件要求
- Arduino板卡
- Micro Servo 9G舵机
- 连接线
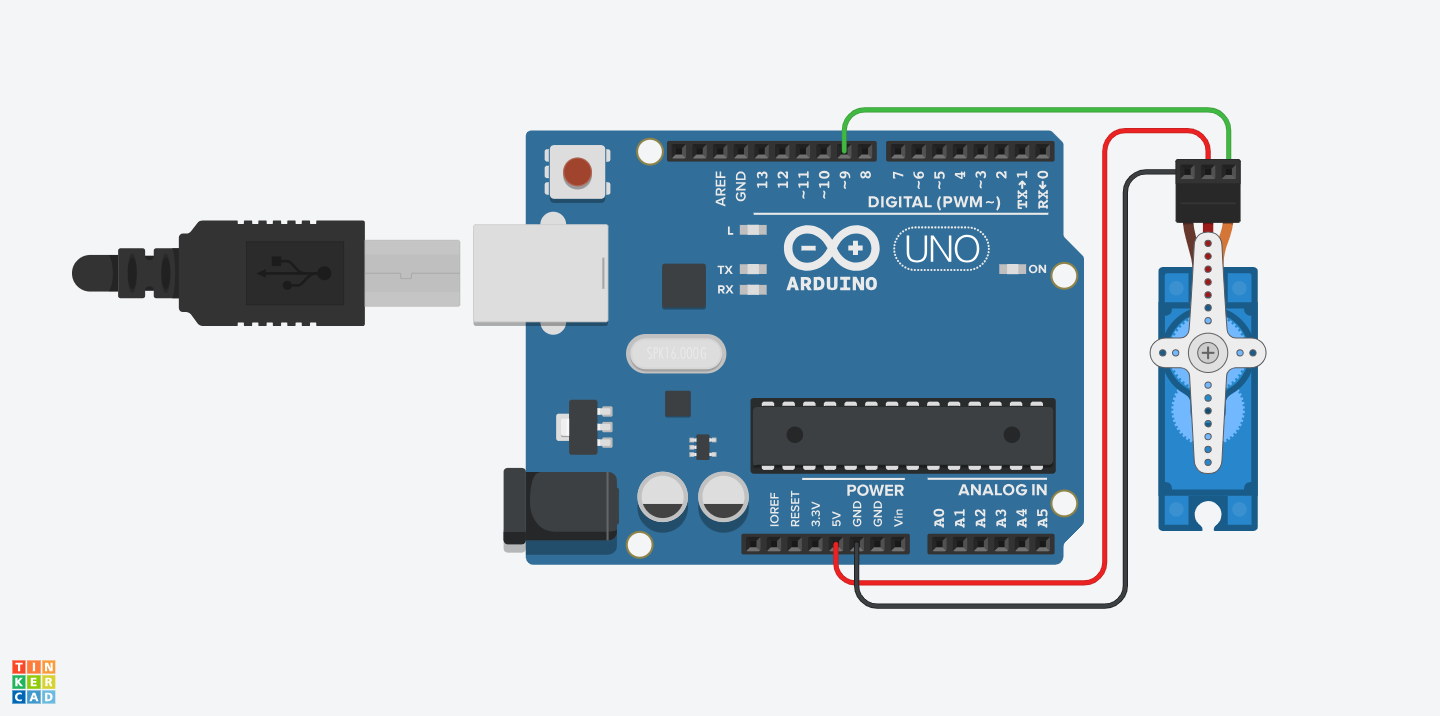
电路
按照舵机的数据表,舵机有棕红橙三根不同颜色的线,分别对应GND、+5V和PWM控制信号,控制信号我们选引脚9。
电路图
代码
调用C/C++类库,我们需要经过以下几个步骤:
- 加载类库的头文件'*.h'
- 指定需要加载的类库文件所在的路径
- 编译类库文件为.a并存放到指定输出目录下
- 生成需要调用的函数的绑定文件
- 在编译时链接库文件并生成可执行文件 为了实现以上目标,我们需要使用两个类库:
- crate::cc用于编译
- crate::bindgen用于生成绑定文件
首先,我们在项目根目录下编写一个配置文件
arduino.yaml,以配置编译过程和绑定代码的生成过程
指定Arduino的安装目录,不同的系统安装目录各有不同,请参考对应平台的安装文档或者IDE中的类库加载路径配置。
Arduino主目录和外部库的安装目录
# Home path for aruduino and external libraries
arduino_home: $HOME/Library/Arduino15
external_libraries_home: $HOME/Documents/Arduino/libraries
SDK版本信息、板卡类型信息和avr-gcc版本信息
# version and board info
core_version: 1.8.6
variant: eightanaloginputs
avr_gcc_version: 7.3.0-atmel3.6.1-arduino7
需要加载的Arduino类库和外部类库
Home path for aruduino and external libraries
# libraries to load
arduino_libraries:
- Wire
external_libraries:
- Servo
为了解析配置文件,我们需要增加一个包在编译时进行处理,修改Cargo.toml
[build-dependencies]
...
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_yaml = "0.9"
...
按照配置的格式,我们增加一个Config类型来承载配置文件解析的结果
struct Config {
pub arduino_home: String,
pub external_libraries_home: String,
pub core_version: String,
pub variant: String,
pub avr_gcc_version: String,
pub arduino_libraries: Vec<String>,
pub external_libraries: Vec<String>,
...
}为配置文件实现一系列在编译和绑定时需要使用的路径方法
impl Config {
fn arduino_package_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
let expanded = envmnt::expand(&self.arduino_home, None);
let arduino_home_path = PathBuf::from(expanded);
arduino_home_path.join("packages").join("arduino")
}
fn core_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.arduino_package_path()
.join("hardware")
.join("avr")
.join(&self.core_version)
}
fn avr_gcc_home(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.arduino_package_path()
.join("tools")
.join("avr-gcc")
.join(&self.avr_gcc_version)
}
fn avg_gcc(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.avr_gcc_home().join("bin").join("avr-gcc")
}
fn arduino_core_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.core_path().join("cores").join("arduino")
}
fn arduino_include_dirs(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let variant_path = self.core_path().join("variants").join(&self.variant);
let avr_gcc_include_path = self.avr_gcc_home().join("avr").join("include");
vec![self.arduino_core_path(), variant_path, avr_gcc_include_path]
}
fn arduino_libraries_path(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let library_root = self.core_path().join("libraries");
let mut result = vec![];
for library in &self.arduino_libraries {
result.push(library_root.join(library).join("src"));
}
result
}
fn external_libraries_path(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let expanded = envmnt::expand(&self.external_libraries_home, None);
let external_library_root = PathBuf::from(expanded);
let mut result = vec![];
for library in &self.external_libraries {
result.push(external_library_root.join(library).join("src"));
}
result
}
fn include_dirs(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let mut result = self.arduino_include_dirs();
result.extend(self.arduino_libraries_path());
result.extend(self.external_libraries_path());
result
}
...
}计算需要监控的项目文件,以在变更后重新编译
impl Config {
...
fn project_files(&self, patten: &str) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let mut result =
files_in_folder(self.arduino_core_path().to_string_lossy().as_ref(), patten);
let mut libraries = self.arduino_libraries_path();
libraries.extend(self.external_libraries_path());
let pattern = format!("**/{}", patten);
for library in libraries {
let lib_sources = files_in_folder(library.to_string_lossy().as_ref(), &pattern);
result.extend(lib_sources);
}
result
}
fn cpp_files(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
self.project_files("*.cpp")
}
fn c_files(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
self.project_files("*.c")
}
...
}遍历目录中的文件
fn files_in_folder(folder: &str, pattern: &str) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let cpp_pattern = format!("{}/{}", folder, pattern);
let mut results = vec![];
for cpp_file in glob(&cpp_pattern).unwrap() {
let file = cpp_file.unwrap();
if !file.ends_with("main.cpp") {
results.push(file);
}
}
results
}为此,我们需要新增一个crate blob
[build-dependencies]
...
glob = "0.3"
...
让Cargo监控当前文件变化,在发生改变时重新执行
// Rebuild if config file changed
println!("cargo:rerun-if-changed={}", CONFIG_FILE); 读取并解析配置文件
let config_string = std::fs::read_to_string(CONFIG_FILE)
.unwrap_or_else(|e| panic!("Unable to read {} file: {}", CONFIG_FILE, e));
let config: Config = serde_yaml::from_str(&config_string)
.unwrap_or_else(|e| panic!("Unable to parse {} file: {}", CONFIG_FILE, e));接下来,我们加入编译依赖cc,以编译C/C++类库文件到target文件夹,为链接生成二进制文件做准备。
我们在进行编译时,需要向编译器传递下列参数并指定编译标志,我们也加入配置文件arduino.yaml中,其中-mmcu指定了微控制器的型号,这样avr-gcc才能为合适的target输出编译后的机器码。
...
# Compile parameters and flags
definitions:
ARDUINO: "10807"
F_CPU: 16000000L
ARDUINO_AVR_UNO: "1"
ARDUINO_ARCH_AVR: "1"
flags:
- "-mmcu=atmega328p"
先要配置编译器
fn configure_arduino(config: &Config) -> Build {
let mut builder = Build::new();
for (k, v) in &config.definitions {
builder.define(k, v.as_str());
}
for flag in &config.flags {
builder.flag(flag);
}
builder
.compiler(config.avg_gcc())
.flag("-Os")
.cpp_set_stdlib(None)
.flag("-fno-exceptions")
.flag("-ffunction-sections")
.flag("-fdata-sections");
for include_dir in config.include_dirs() {
builder.include(include_dir);
}
builder添加类库源文件到Cargo的监视目标,在更新后会使类库重新编译
pub fn add_source_file(builder: &mut Build, files: Vec<PathBuf>) {
for file in files {
println!("cargo:rerun-if-changed={}", file.to_string_lossy());
builder.file(file);
}
}编译C/C++类库,按照命名规范,类库名称用lib开头
fn compile_arduino(config: &Config) {
let mut builder = configure_arduino(&config);
builder
.cpp(true)
.flag("-std=gnu++11")
.flag("-fpermissive")
.flag("-fno-threadsafe-statics");
add_source_file(&mut builder, config.cpp_files());
builder.compile("libarduino_c++.a");
let mut builder = configure_arduino(&config);
builder.flag("-std=gnu11");
add_source_file(&mut builder, config.c_files());
builder.compile("libarduino_c.a");
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=static=arduino_c++");
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=static=arduino_c");
}在main函数里加载编译过程
compile_arduino(&config);我们还需要为类库里的类型和方法生成绑定,才能够在Rust代码里直接调用。绑定可以手动编写,也可以通过工具bindgen生成。这里需要注意的是,bindgen只能很好的根据C类库的.h头文件生成绑定,而对于C++代码,会存在一定的无法解析的情况,对于无法解析的代码,他会自动略过,而且无法有效解析C++的声明和实现混合的.hpp头文件。
我们在项目根目录下编写一个wrapper.h文件,这样可以有效的控制我们需要编译和绑定哪些头文件,对于头文件中包含的代码指向的其它源文件和头文件,将会递归检索。
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Servo.h>
配置bindgen,传入板卡参数和微控制器的信号,指定文件包含路径,以及指定需要生成和屏蔽的函数和方法的绑定
fn configure_bindgen_for_arduino(config: &Config) -> Builder {
let mut builder = Builder::default();
for (k, v) in &config.definitions {
builder = builder.clang_arg(&format!("-D{}={}", k, v));
}
for flag in &config.flags {
builder = builder.clang_arg(flag);
}
builder = builder
.clang_args(&["-x", "c++", "-std=gnu++11"])
.use_core()
.header("wrapper.h")
.layout_tests(false)
.parse_callbacks(Box::new(bindgen::CargoCallbacks::new()));
for include_dir in config.include_dirs() {
builder = builder.clang_arg(&format!("-I{}", include_dir.to_string_lossy()));
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.allowlist_function {
builder = builder.allowlist_function(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.allowlist_type {
builder = builder.allowlist_type(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.blocklist_function {
builder = builder.blocklist_function(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.blocklist_type {
builder = builder.blocklist_type(item);
}
builder
}因为这里我们只需要使用Servo类型及其方法,所以,我们可以在arduino.yaml配置文件中增加如下配置
...
# binding filter
bindgen_lists:
allowlist_function:
# - Arduino.*
- Servo.*
allowlist_type:
- Servo.*
blocklist_function:
- Print.*
- String.*
blocklist_type:
- Print.*
- String.*
生成绑定并输出到项目target的OUT_DIR
fn generate_bindings(config: &Config) {
let bindings: Bindings = configure_bindgen_for_arduino(&config)
.generate()
.expect("Unable to generate bindings");
let out_path = PathBuf::from(env::var("OUT_DIR").unwrap());
bindings
.write_to_file(out_path.join("bindings.rs"))
.expect("Couldn't write bindings!");
}在main函数里加载编译过程
compile_arduino(&config);为项目增加编译依赖项
[build-dependencies]
...
cc = "1.0.96"
bindgen = "0.69.4"
以上,我们就编写好了build.rs来扩展cargo的编译过程了。
完整代码如下:
arduino.yaml
# Home path for aruduino and external libraries
arduino_home: $HOME/Library/Arduino15
external_libraries_home: $HOME/Documents/Arduino/libraries
# Version and board info
core_version: 1.8.6
variant: eightanaloginputs
avr_gcc_version: 7.3.0-atmel3.6.1-arduino7
# Libraries to load
arduino_libraries:
- Wire
external_libraries:
- Servo
# Compile parameters and flags
definitions:
ARDUINO: "10807"
F_CPU: 16000000L
ARDUINO_AVR_UNO: "1"
ARDUINO_ARCH_AVR: "1"
flags:
- "-mmcu=atmega328p"
# binding filter
bindgen_lists:
allowlist_function:
# - Arduino.*
- Servo.*
allowlist_type:
- Servo.*
blocklist_function:
- Print.*
- String.*
blocklist_type:
- Print.*
- String.*
build.rs
use std::{collections::HashMap, env, path::PathBuf};
use bindgen::{Bindings, Builder};
use cc::Build;
use glob::glob;
use serde::Deserialize;
const CONFIG_FILE: &str = "arduino.yaml";
fn main() {
// Rebuild if config file changed
println!("cargo:rerun-if-changed={}", CONFIG_FILE);
let config_string = std::fs::read_to_string(CONFIG_FILE)
.unwrap_or_else(|e| panic!("Unable to read {} file: {}", CONFIG_FILE, e));
let config: Config = serde_yaml::from_str(&config_string)
.unwrap_or_else(|e| panic!("Unable to parse {} file: {}", CONFIG_FILE, e));
println!("Arduino configuration: {:#?}", config);
println!(
"arduino_library_path:{:#?}\nexternal_library_path:{:#?}",
config.arduino_libraries_path(),
config.external_libraries_path()
);
compile_arduino(&config);
generate_bindings(&config);
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct BindgenLists {
pub allowlist_function: Vec<String>,
pub allowlist_type: Vec<String>,
pub blocklist_function: Vec<String>,
pub blocklist_type: Vec<String>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Deserialize)]
struct Config {
pub arduino_home: String,
pub external_libraries_home: String,
pub core_version: String,
pub variant: String,
pub avr_gcc_version: String,
pub arduino_libraries: Vec<String>,
pub external_libraries: Vec<String>,
pub definitions: HashMap<String, String>,
pub flags: Vec<String>,
pub bindgen_lists: BindgenLists,
}
impl Config {
fn arduino_package_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
let expanded = envmnt::expand(&self.arduino_home, None);
let arduino_home_path = PathBuf::from(expanded);
arduino_home_path.join("packages").join("arduino")
}
fn core_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.arduino_package_path()
.join("hardware")
.join("avr")
.join(&self.core_version)
}
fn avr_gcc_home(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.arduino_package_path()
.join("tools")
.join("avr-gcc")
.join(&self.avr_gcc_version)
}
fn avg_gcc(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.avr_gcc_home().join("bin").join("avr-gcc")
}
fn arduino_core_path(&self) -> PathBuf {
self.core_path().join("cores").join("arduino")
}
fn arduino_include_dirs(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let variant_path = self.core_path().join("variants").join(&self.variant);
let avr_gcc_include_path = self.avr_gcc_home().join("avr").join("include");
vec![self.arduino_core_path(), variant_path, avr_gcc_include_path]
}
fn arduino_libraries_path(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let library_root = self.core_path().join("libraries");
let mut result = vec![];
for library in &self.arduino_libraries {
result.push(library_root.join(library).join("src"));
}
result
}
fn external_libraries_path(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let expanded = envmnt::expand(&self.external_libraries_home, None);
let external_library_root = PathBuf::from(expanded);
let mut result = vec![];
for library in &self.external_libraries {
result.push(external_library_root.join(library).join("src"));
}
result
}
fn include_dirs(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let mut result = self.arduino_include_dirs();
result.extend(self.arduino_libraries_path());
result.extend(self.external_libraries_path());
result
}
fn project_files(&self, patten: &str) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let mut result =
files_in_folder(self.arduino_core_path().to_string_lossy().as_ref(), patten);
let mut libraries = self.arduino_libraries_path();
libraries.extend(self.external_libraries_path());
let pattern = format!("**/{}", patten);
for library in libraries {
let lib_sources = files_in_folder(library.to_string_lossy().as_ref(), &pattern);
result.extend(lib_sources);
}
result
}
fn cpp_files(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
self.project_files("*.cpp")
}
fn c_files(&self) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
self.project_files("*.c")
}
}
fn files_in_folder(folder: &str, pattern: &str) -> Vec<PathBuf> {
let cpp_pattern = format!("{}/{}", folder, pattern);
let mut results = vec![];
for cpp_file in glob(&cpp_pattern).unwrap() {
let file = cpp_file.unwrap();
if !file.ends_with("main.cpp") {
results.push(file);
}
}
results
}
fn configure_arduino(config: &Config) -> Build {
let mut builder = Build::new();
for (k, v) in &config.definitions {
builder.define(k, v.as_str());
}
for flag in &config.flags {
builder.flag(flag);
}
builder
.compiler(config.avg_gcc())
.flag("-Os")
.cpp_set_stdlib(None)
.flag("-fno-exceptions")
.flag("-ffunction-sections")
.flag("-fdata-sections");
for include_dir in config.include_dirs() {
builder.include(include_dir);
}
builder
}
pub fn add_source_file(builder: &mut Build, files: Vec<PathBuf>) {
for file in files {
println!("cargo:rerun-if-changed={}", file.to_string_lossy());
builder.file(file);
}
}
fn compile_arduino(config: &Config) {
let mut builder = configure_arduino(&config);
builder
.cpp(true)
.flag("-std=gnu++11")
.flag("-fpermissive")
.flag("-fno-threadsafe-statics");
add_source_file(&mut builder, config.cpp_files());
builder.compile("libarduino_c++.a");
let mut builder = configure_arduino(&config);
builder.flag("-std=gnu11");
add_source_file(&mut builder, config.c_files());
builder.compile("libarduino_c.a");
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=static=arduino_c++");
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=static=arduino_c");
}
fn configure_bindgen_for_arduino(config: &Config) -> Builder {
let mut builder = Builder::default();
for (k, v) in &config.definitions {
builder = builder.clang_arg(&format!("-D{}={}", k, v));
}
for flag in &config.flags {
builder = builder.clang_arg(flag);
}
builder = builder
.clang_args(&["-x", "c++", "-std=gnu++11"])
.use_core()
.header("wrapper.h")
.layout_tests(false)
.parse_callbacks(Box::new(bindgen::CargoCallbacks::new()));
for include_dir in config.include_dirs() {
builder = builder.clang_arg(&format!("-I{}", include_dir.to_string_lossy()));
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.allowlist_function {
builder = builder.allowlist_function(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.allowlist_type {
builder = builder.allowlist_type(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.blocklist_function {
builder = builder.blocklist_function(item);
}
for item in &config.bindgen_lists.blocklist_type {
builder = builder.blocklist_type(item);
}
builder
}
fn generate_bindings(config: &Config) {
let bindings: Bindings = configure_bindgen_for_arduino(&config)
.generate()
.expect("Unable to generate bindings");
let out_path = PathBuf::from(env::var("OUT_DIR").unwrap());
bindings
.write_to_file(out_path.join("bindings.rs"))
.expect("Couldn't write bindings!");
}在使用时,我们需要修改libs.rs,因为一个rust项目只允许有一个libs文件,所以我们需要通过include宏将绑定文件的内容合并到libs中。由于C/C++类库和Rust类库的命名规范不一致,所以,我们这里要使用属性宏允许绑定文件中出现不符合命名规范的函数和类型。
#![allow(non_snake_case)]
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/bindings.rs"));之后,我们需要在Rust源代码里面初始化Arduino类库的初始化过程,这需要用到Arduino.h中包含的init()方法。因为我们已经编译了Arduino类库,所以,我们只需要在引入这个方法。
extern "C" {
fn init();
}到这里,我们便可以在Rust里直接使用Arduino的类库类型和函数了。
完整代码如下: src/main.rs
/*!
* Servo Control
*
* Sweep a standard SG90 compatible servo from its left limit all the way to its right limit and back.
*/
#![no_std]
#![no_main]
use arduino_hal::delay_ms;
use arduino_uno_example::Servo;
use avr_device::entry;
use panic_halt as _;
extern "C" {
fn init();
}
#[entry]
fn main() -> ! {
unsafe {
init();
}
unsafe {
let mut myservo = Servo::new();
myservo.attach(9);
loop {
for degree in (0..=180).chain((0..179).rev()) {
myservo.write(degree);
delay_ms(15)
}
}
}
}编译并运行示例
cargo build
cargo run
此时,我们可以看到,舵机开始移动到0度,之后每次移动∼1度